Mất password Admin Domain ư !!!. Điều đáng tiếc này có thể xảy ra khi Admin tiến hành thay đổi password mới theo định kỳ nhằm tăng cường hơn nữa an toàn cho hệ thống, nhưng đáng tiếc ví một lý do nào đó, họ đã quên password mới của mình. Và kết quả là họ không còn log-on vào Domain Controller của mình được nữa, và họ cũng không tạo bất cứ một backup admin account nào dự phòng cho việc quên password này...
Một vài thủ thuật và công cụ đã được công bố giúp reset lại Domain Admin Password trên Windows 2000 Server đã không còn bất ký tác dụng nào trên Windows 2003 Server. Lý do, Microsoft đã áp dụng tăng cường mọi mặt các tính năng bảo mật trên Windows 2003 Server, và những thủ thuật nà đã trở nên vô tác dụng.
Sau đây là cách thức thiết lập lại Domin AdminPassword account. Và trước khi các bạn tiến hành nó, hãy chú ý kỹ tất cả các yêu cầu bắt buộc dưới đây :
Khuyến cáo: Tài liệu hướng dẫn này chỉ để giúp Admin khắc phục sự cố do chính mình gây ra. Tài liệu không phục vụ cho bất kỳ ý đồ bất minh nào để thực hiện xâm nhập vào hệ thống !
Các yêu cầu bắt buộc :
Bạn cần đáp ứng các yêu cầu sau:
1/ Truy cập cục bộ-Local access vào máy chủ Domain Controller (DC).
2/ Có được Local Administrator password (đây chính là Active Directory Restore mode password bạn xác lập trong quá trình tiến hành nâng một Server 2003 lên thành Domain Controller 2003, password này hoàn toàn khác với password điều khiển hoạt động của máy chủ DC và Domain- password mà bạn đã quên).
3/ Có 2 công cụ được cung cấp bởi Microsoft trong bộ Resource Kit: SRVANY và INSTSRV. Download ở đây
Tất cả các bước tiến hành này đều thực hiện trên một domain với một máy chủ Domain Controller 2003. Nếu domain của bạn có nhiều DCs, có thể chọn bất kỳ Domain Controller nào để thực hiện.
Tiến hành:
1. Khởi động lại DC Windows 2003 trong chế độ Directory Restory Service Mode.
Khởi động lại máy,tại thời điểm startup, nhấn F8và chọn Directory Restore Service Mode. Khi vào chế độ này hoạt động của Active Directory sẽ bị disable.
Khi màn hình login xuất hiện, log on vào với tài khoản Local Administrator. Và bạn đã có toàn quyền truy cập Local Computer này nhưng không thể can thiệp vào bất cứ vấn đề gì thuộc Active Directory.
2 Tiến hành cài đặt SRVANY.
Tiện ích này vận hành Windows NT Service. Và điều thú vị ở đây là chương trình sẽ có các đặc quyền hệ thống- SYSTEM privileges. Và điều này là cần thiết để có thể reset Domain Admin password. Bạn sẽ thực hiện cấu hình SRVANY để khởi hoạt command prompt (sẽ giúp bạn chay các lệnh net user).
Copy SRVANY và INSTSRV vào một folder tạm thời, ví dụ d:temp. Cũng Copy cmd.exe vào folder này (cmd.exe chình là command prompt, thường nằm ở %WINDIR%System32, ví dụ như : C:WindowsSystem32).
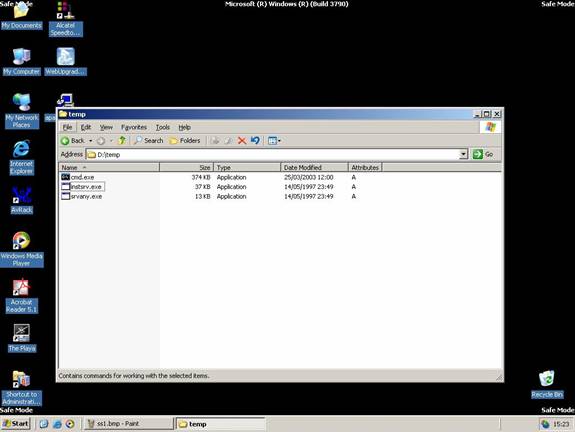
Click vào cmd.exe để khởi hoạt command prompt, gõ lệnh Cd D:temp nhấn Enter , Gõ tiếp lệnh instsrv PassRecovery "d:tempsrvany.exe" nhấn Enter
Cấu hình SRVANY.
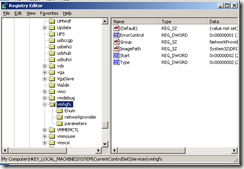
Tại Run gõ lệnh regedit, mở Registry Editor và tìm đến Key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESystemCurrentControlSetServicesP assRecovery
Right-click vào key PassRecovery và tạo một Key con Parameters và add vào 2 values mới như sau:
name: Application
type: REG_SZ (string)
value: d:tempcmd.exe
name: AppParameters
type: REG_SZ (string)
value: /k net user administrator new_password
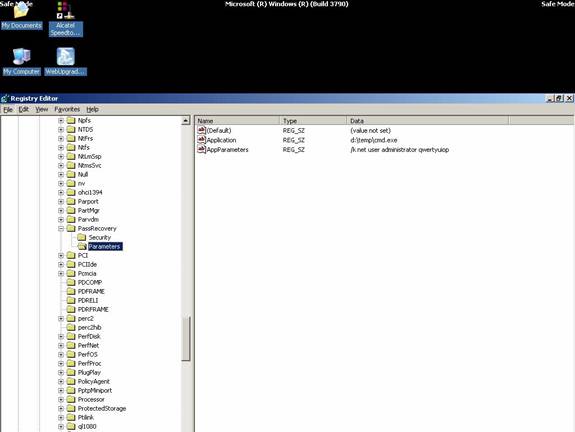
Cẩn thận: 'net user username password' chính là command line để xác lập một new password. Thay thế new_password với password thực sự mà bạn muốn đặt mới. Ghi nhớ rằng một số chính sách của domain- domain policies, có thể yêu cầu bạn phải đặt password phức hợp( complex passwords), do vậy bạn phải đặt password phức hơp thường gồm có chữ Hoa, thường, Số và các ký tự đặc biệt, ví dụ : p@ssW0rd!#$
Tiếp theo tại Run, gõ lệnh Services.msc hoặc vào Control PanelAdministrative ToolsServices sẽ mở bảng điều khiển các dịch vụ vận hành trên hệ thống. Tìm đến Service có tên PassRecovery, right-click chọn property tab. Kiểm tra start mode phải là Automatic.
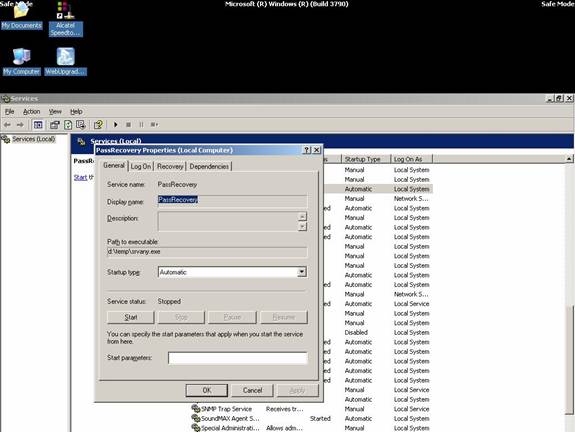
Mở Log On tab và check vào lựa chọn Allow service to interact with desktop. Tại thời điểm này bạn có thể restart Windows, và SRVANY se chạy lệnh netuser command để tiến hành reset lại domain admin password.
3 Khởi động lại Windows ở chế độ thường -normal mode
Chờ khi màn hình login xuất hiện. bạn sẽ không nhận thấy command prompt xuất hiện khi thực hiện lệnh net user command. Nhưng đừng lo lắng, command vẫn được thực thi bên trong hệ thống -background.
Log on với tài khoản Administrator, password bạn vừa xác lập mới ở trên. Hệ thống sẽ ban đầy đủ quyền truy cập cho bạn. Nếu không quay lại bước 2 và đảm bảo rằng bạn không quên password mới đã xác lập hoặc xác lập sai các values khác.
Khi desktop xuất hiện, bạn sẽ thấy command prompt. Command prompt được khởi động bởi SRVANY.
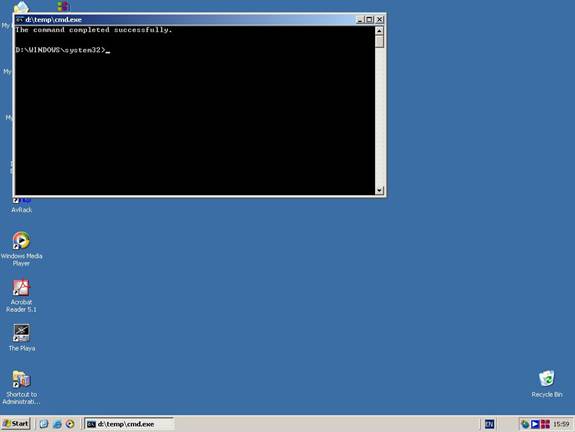
Đến đây đã đạt được mục đích, tiến hành gỡ bỏ SRVANY:
Thực hiện các lệnh:
net stop PassRecovery
sc delete PassRecovery
Xóa tiếp folder d:temp đã tạo. Finished !
(Tham khảo QTM)
Một vài thủ thuật và công cụ đã được công bố giúp reset lại Domain Admin Password trên Windows 2000 Server đã không còn bất ký tác dụng nào trên Windows 2003 Server. Lý do, Microsoft đã áp dụng tăng cường mọi mặt các tính năng bảo mật trên Windows 2003 Server, và những thủ thuật nà đã trở nên vô tác dụng.
Sau đây là cách thức thiết lập lại Domin AdminPassword account. Và trước khi các bạn tiến hành nó, hãy chú ý kỹ tất cả các yêu cầu bắt buộc dưới đây :
Khuyến cáo: Tài liệu hướng dẫn này chỉ để giúp Admin khắc phục sự cố do chính mình gây ra. Tài liệu không phục vụ cho bất kỳ ý đồ bất minh nào để thực hiện xâm nhập vào hệ thống !
Các yêu cầu bắt buộc :
Bạn cần đáp ứng các yêu cầu sau:
1/ Truy cập cục bộ-Local access vào máy chủ Domain Controller (DC).
2/ Có được Local Administrator password (đây chính là Active Directory Restore mode password bạn xác lập trong quá trình tiến hành nâng một Server 2003 lên thành Domain Controller 2003, password này hoàn toàn khác với password điều khiển hoạt động của máy chủ DC và Domain- password mà bạn đã quên).
3/ Có 2 công cụ được cung cấp bởi Microsoft trong bộ Resource Kit: SRVANY và INSTSRV. Download ở đây
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyID=9d467a69-57ff-4ae7-96ee-b18c4790cffd&DisplayLang=en.
Tất cả các bước tiến hành này đều thực hiện trên một domain với một máy chủ Domain Controller 2003. Nếu domain của bạn có nhiều DCs, có thể chọn bất kỳ Domain Controller nào để thực hiện.
Tiến hành:
1. Khởi động lại DC Windows 2003 trong chế độ Directory Restory Service Mode.
Khởi động lại máy,tại thời điểm startup, nhấn F8và chọn Directory Restore Service Mode. Khi vào chế độ này hoạt động của Active Directory sẽ bị disable.
Khi màn hình login xuất hiện, log on vào với tài khoản Local Administrator. Và bạn đã có toàn quyền truy cập Local Computer này nhưng không thể can thiệp vào bất cứ vấn đề gì thuộc Active Directory.
2 Tiến hành cài đặt SRVANY.
Tiện ích này vận hành Windows NT Service. Và điều thú vị ở đây là chương trình sẽ có các đặc quyền hệ thống- SYSTEM privileges. Và điều này là cần thiết để có thể reset Domain Admin password. Bạn sẽ thực hiện cấu hình SRVANY để khởi hoạt command prompt (sẽ giúp bạn chay các lệnh net user).
Copy SRVANY và INSTSRV vào một folder tạm thời, ví dụ d:temp. Cũng Copy cmd.exe vào folder này (cmd.exe chình là command prompt, thường nằm ở %WINDIR%System32, ví dụ như : C:WindowsSystem32).

Click vào cmd.exe để khởi hoạt command prompt, gõ lệnh Cd D:temp nhấn Enter , Gõ tiếp lệnh instsrv PassRecovery "d:tempsrvany.exe" nhấn Enter
Cấu hình SRVANY.
Tại Run gõ lệnh regedit, mở Registry Editor và tìm đến Key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESystemCurrentControlSetServicesP assRecovery
Right-click vào key PassRecovery và tạo một Key con Parameters và add vào 2 values mới như sau:
name: Application
type: REG_SZ (string)
value: d:tempcmd.exe
name: AppParameters
type: REG_SZ (string)
value: /k net user administrator new_password

Cẩn thận: 'net user username password' chính là command line để xác lập một new password. Thay thế new_password với password thực sự mà bạn muốn đặt mới. Ghi nhớ rằng một số chính sách của domain- domain policies, có thể yêu cầu bạn phải đặt password phức hợp( complex passwords), do vậy bạn phải đặt password phức hơp thường gồm có chữ Hoa, thường, Số và các ký tự đặc biệt, ví dụ : p@ssW0rd!#$
Tiếp theo tại Run, gõ lệnh Services.msc hoặc vào Control PanelAdministrative ToolsServices sẽ mở bảng điều khiển các dịch vụ vận hành trên hệ thống. Tìm đến Service có tên PassRecovery, right-click chọn property tab. Kiểm tra start mode phải là Automatic.

Mở Log On tab và check vào lựa chọn Allow service to interact with desktop. Tại thời điểm này bạn có thể restart Windows, và SRVANY se chạy lệnh netuser command để tiến hành reset lại domain admin password.
3 Khởi động lại Windows ở chế độ thường -normal mode
Chờ khi màn hình login xuất hiện. bạn sẽ không nhận thấy command prompt xuất hiện khi thực hiện lệnh net user command. Nhưng đừng lo lắng, command vẫn được thực thi bên trong hệ thống -background.
Log on với tài khoản Administrator, password bạn vừa xác lập mới ở trên. Hệ thống sẽ ban đầy đủ quyền truy cập cho bạn. Nếu không quay lại bước 2 và đảm bảo rằng bạn không quên password mới đã xác lập hoặc xác lập sai các values khác.
Khi desktop xuất hiện, bạn sẽ thấy command prompt. Command prompt được khởi động bởi SRVANY.

Đến đây đã đạt được mục đích, tiến hành gỡ bỏ SRVANY:
Thực hiện các lệnh:
net stop PassRecovery
sc delete PassRecovery
Xóa tiếp folder d:temp đã tạo. Finished !
(Tham khảo QTM)